Recognizing Nephrology Symptoms: Understanding Kidney Health

Our kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining overall health by filtering waste products, balancing fluids, and regulating electrolytes in our bodies. When kidney function is compromised, it can lead to a range of symptoms that often go unnoticed until the condition becomes severe.
Understanding these symptoms is essential for early detection and treatment of kidney-related issues. In this blog, we will explore common nephrology symptoms and their implications.
Swelling in Both Feet and Legs
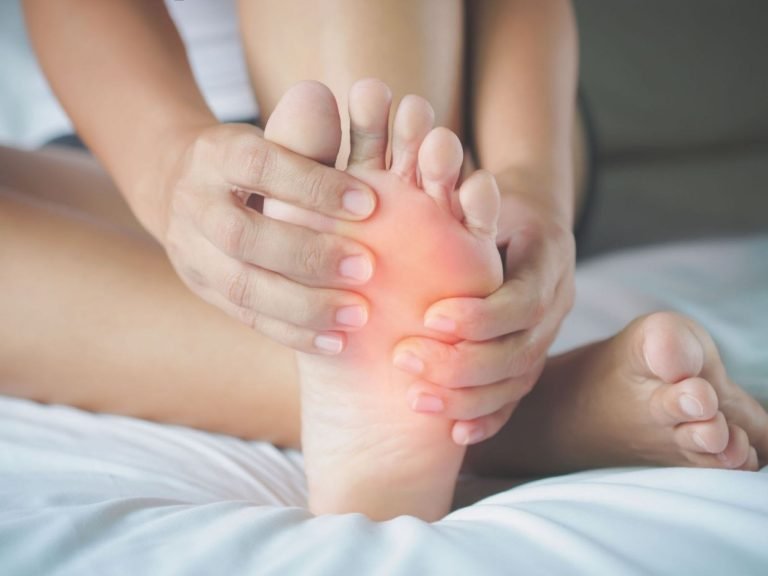
Swelling, also known as edema, in the feet and legs is often one of the earliest signs of kidney dysfunction. The kidneys help manage fluid balance in the body, and when they are not functioning properly, excess fluid can accumulate in the tissues. This swelling may also be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort.
Note-to-Patients: water for decreased urine output, Breathing difficulty, abdominal distension, frothy urine & difficulty in breathing on exertion, when you have swelling of your legs & feet.
Puffy Face

A puffy or swollen face, especially around the eyes, particularly in the morning, is another common symptom of kidney problems. This occurs because of fluid retention, which is often a result of the kidneys’ inability to remove excess water and waste from the blood. This symptom is frequently associated with nephrotic syndrome, a kidney disorder that causes the body to excrete too much protein in the urine.
Note-to-Patients: Water For accompanying blood in urine, skin rashes, and weight changes.
Frothy Urine
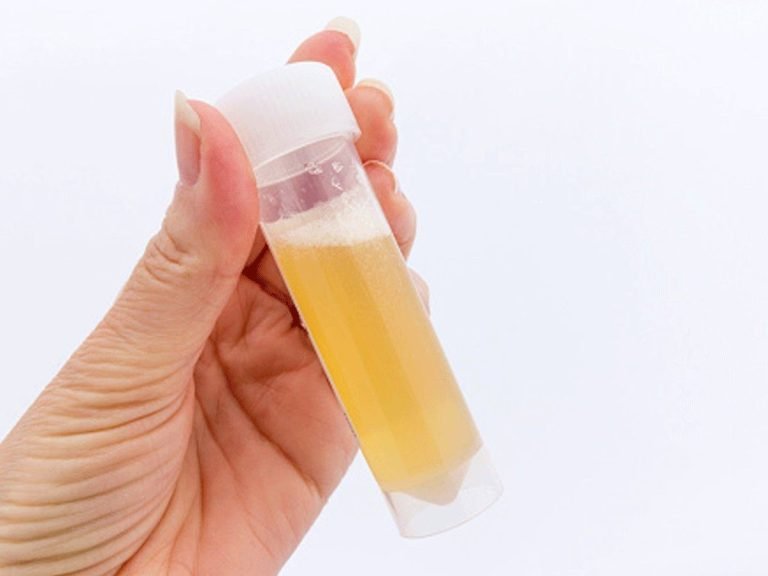
Frothy or foamy urine is a sign of proteinuria, where excess protein is present in the urine. This condition indicates that the kidneys’ filtering units, called glomeruli, are damaged and allow protein to leak into the urine. Persistent frothy urine warrants medical attention, as it can signal serious kidney issues.
Burning Sensation or Pain During Urination
A burning sensation or pain during urination typically indicates a urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs can affect any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys. If left untreated, a UTI can lead to kidney infections (pyelonephritis), which can cause permanent damage to the kidneys and other serious health complications.
Note to patients: Definite evaluation of UTI, is required for pregnant women, men, Diabetic
Blood in Urine
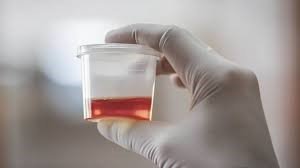
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be alarming and is a symptom that should not be ignored. It can result from various conditions, including kidney stones, infections, and in more severe cases, kidney disease or cancer. The blood can make the urine appear pink, red, or cola-coloured.
Note-to-Patients: Hematuria Due to any cause requires urgent evaluation to prevent permanent kidney damage.
Reduced Urine Output
A significant reduction in urine output, also known as oliguria, is a concerning sign of kidney failure. This can result from severe dehydration, obstruction in the urinary tract, or acute kidney injury. If you notice a substantial decrease in urine production, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation immediately.
The need For Conservative Management Vs dialysis has to be evaluated to prevent life-threatening complications.
Shortness of Breath
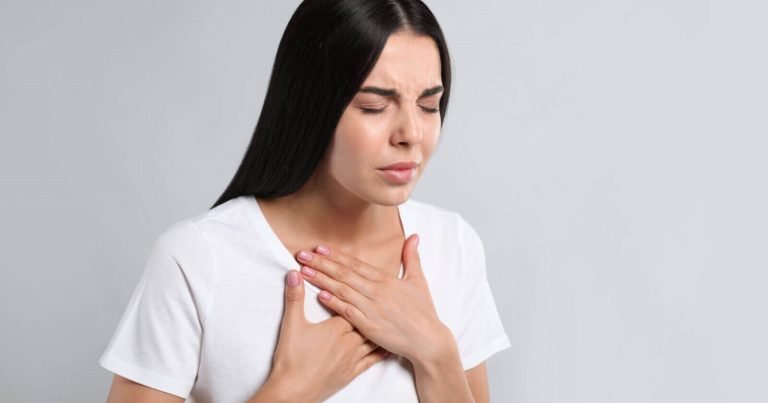

Shortness of breath can be indirectly related to kidney problems. When the kidneys fail to remove enough fluid, it can accumulate in the lungs, causing pulmonary edema. Additionally, anemia, a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD), can also lead to shortness of breath due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Regular cardiac evaluations are also needed to prevent any cardiac events, especially in patients with CKD.
Lower Back Pain During Urination
Pain in the lower back during urination can indicate a kidney infection or kidney stones. Kidney infections often present with a sharp, stabbing pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin. Kidney stones, on the other hand, cause intense pain as they move through the urinary tract, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting, With occasional blood in the urine.
Fever with Chills
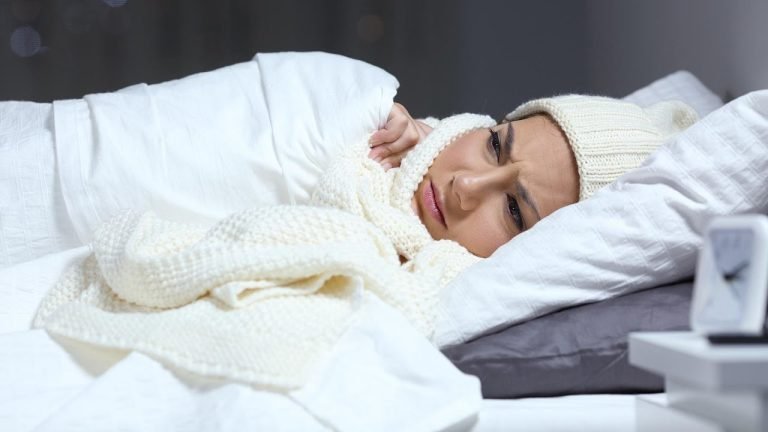

A fever with chills is a common symptom of an infection, including kidney infections. Pyelonephritis, a type of kidney infection, often presents with high fever, chills, back or side pain, nausea, and vomiting. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent complications.
Loss of Appetite, Nausea, and Vomiting
These gastrointestinal symptoms can be related to advanced kidney disease. When the kidneys are unable to filter waste products efficiently, toxins build up in the blood, leading to nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. This condition, known as uremia, can also cause a metallic taste in the mouth and breath that smells like ammonia.
Family History of Kidney Disease
A family history of kidney disease increases the risk of developing kidney problems. Genetic factors play a significant role in conditions like polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and Alport syndrome. Individuals with a family history of kidney disease should undergo regular check-ups and maintain a healthy lifestyle to mitigate risks.
Hypertension or Diabetes, With or Without Kidney Disease
Hypertension (high blood pressure) and diabetes are the leading causes of kidney disease. These conditions damage the blood vessels in the kidneys over time, reducing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids. Managing blood pressure and blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing or slowing the progression of kidney disease. Prevention is better than cure this holds good in diabetes & hypertension. Why wait till you develop a Kidney disease? Regular screening of HTM & diabetics is of utmost importance to prevent kidney disease.
Hypertension During Pregnancy
Pregnancy-induced hypertension, or preeclampsia, can affect kidney function. This condition is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine during pregnancy. Preeclampsia can lead to serious complications for both the mother and baby, and it requires careful monitoring and management by healthcare professionals.
Symptoms of Lower Back Pain During Urination
- Sharp or Dull Pain: The pain can range from a sharp, stabbing sensation to a dull, constant ache in the lower back.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation during urination is often present, indicating a potential urinary tract infection (UTI).
- Frequent Urination: An increased need to urinate more often than usual.
- Urgency: A strong, sudden urge to urinate, which can be difficult to control.
- Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Urine that appears cloudy or has a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Blood in Urine: The presence of blood in the urine, which can appear pink, red, or brownish.
- Fever and Chills: A fever or chills can accompany these symptoms, especially if an infection is present.
- Discomfort in the Abdomen or Pelvis: Pain or discomfort may also be felt in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting can be associated with severe infections or kidney issues.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness or malaise.
History of Kidney Stones
A history of kidney stones increases the risk of recurrent stone formation and potential kidney damage. Kidney stones can obstruct the urinary tract, leading to pain, infections, and decreased kidney function. Preventive measures, such as staying hydrated and avoiding certain foods, can help reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Regular Use of Painkillers or Traditional Medication
Long-term use of certain painkillers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can harm the kidneys. These medications can reduce blood flow to the kidneys, leading to acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease over time. Similarly, some traditional or herbal medications may contain substances that are toxic to the kidneys. It’s important to use medications as prescribed and consult a healthcare provider about any potential risks.
Existing Cardiac Conditions
Heart and kidney health are closely linked. Conditions such as heart failure and coronary artery disease can impair kidney function. Conversely, kidney disease can exacerbate heart problems by increasing blood pressure and causing fluid retention. Managing both heart and kidney health through lifestyle changes and medical treatments is essential for overall well-being.
Recognizing the symptoms of kidney problems is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly.
Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and managing underlying conditions like hypertension and diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of kidney disease.
By being aware and proactive, we can ensure our kidneys continue to function effectively and contribute to our overall health and well-being.















